|
Presentation Number:
|
1015-126
|
|
Abstract Title:
|
Biventricular Pacing Reduces Incidence of Microvolt T Wave Alternans
in Patients With Congestive Heart Failure
|
|
Presentation Start/End Time:
|
Tuesday, Mar 14, 2006, 2:30 PM - 3:30 PM
|
|
Topic:
|
Cardiac Pacing
|
|
Author Block:
|
Safwat A. Gassis, Fernando Mera,
David B. DeLurgio, Paul F. Walter, Jonathan J. Langberg, Angel R. Leon,
Carlyle Fraser Heart Center, Emory University, Atlanta, GA
|
|
Background: Microvolt T-Wave
alternans (MTWA) is a useful non-invasive tool to asses risk for malignant
ventricular arrhythmias. Cardiac resynchronization (CRT) with biventricular
pacing (BiV) has been shown to improve hemodynamics and may reduce the risk
of sudden cardiac death. The purpose of the current study was to determine
the effect of CRT on MTWA.
Methods: Twenty two patients underwent implantation of a CRT device
(9 ischemic, mean ejection fraction 18 +/- 7%). MTWA was measured during
atrial pacing, DDD pacing with only right ventricular (RV) activation, and
during DDD pacing with biventricular pacing in an integrated bipolar
configuration.
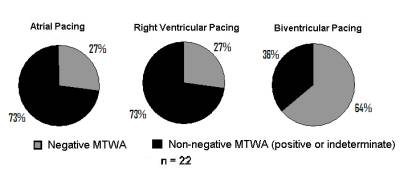
Results: MTWA during atrial pacing was positive in 55%, negative in
27% and indeterminate in 18% of patients. MTWA results were dichotomized
into negative and non-negative categories. BiV pacing increased the
incidence of negative MTWA from 27% with atrial pacing to 64%. Overall MTWA
concordance between atrial and BiV pacing was 55% whereas concordance
between atrial and RV pacing was 73%. Concordance of atrial or RV pacing
with BiV pacing was 44% for positive or indeterminate tests compared to 83%
for negative MTWA tests.
Conclusion: MTWA measurement during BiV pacing is feasible and
reduces the proportion of positive or indeterminate results whereas atrial
and RV pacing is more likely to lead to non-negative results. Whether the
shift to a negative MTWA test during BiV pacing truly represents a decrease
in risk for ventricular arrhythmia remains to be determined.
|
|
Keywords:
|
Cardiac resynchronization,Arrhythmias,Electrophysiology
|
|
|
|