Predictive Value of T-wave Alternans Recorded from Electrograms of
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator
Category: 33 Device Technology
Presentation Time: Wednesday, 5:45 p.m. - 7:00 p.m.
Presentation Number: P1-66
Keyword: T-wave alternans, Implantable
cardioverter-defibrillator
Microvolt T-wave alternans (TWA) on the surface ECG increases acutely
prior to VT/VF in animals, suggesting that TWA recorded from ICD electrograms
(EGMs) may warn of VT/VF in ICD pts. We have shown TWA has greater amplitude on
ICD EGMs than on the ECG. But it is not known if EGM TWA represents the same
pathophysiological process as ECG TWA, which is a good long-term predictor of
spontaneous VT/VF. This study investigated the predictive value of EGM and ECG
TWA. Methods: In 25 pts with dual-chamber ICDs and intact AV conduction,
we recorded TWA during trials of atrial and AV pacing. Each trial consisted of
3 min of pacing at each of 3 rates (80, 95, and 110 bpm) for a total of 9 min
per trial. EGM TWA was measured off line by spectral analysis. EGM TWA was
positive (+) if either pacing method produced sustained alternans ≥ 30 μV with K score
(signal-to-noise ratio) ≥ 3. Simultaneously, ECG TWA was analyzed by a
commercial system (CHS2000, Cambridge Heart, Inc). ECG TWA was positive if
either pacing method produced sustained alternans ≥ 1.9 μV with K score
≥ 3. The endpoint was appropriate ICD therapy for VT/VF during follow-up
≥ 6 months. Results: TWA tests were positive in 10 pts (40%) by
ECG and in 13 pts (52%) by EGM. ECG and EGM TWA results were concordant in 21
pts (84%). During median follow-up of 7 months (range 6 - 13 months), 7 pts had
appropriate ICD therapy. Of these, 6 pts had positive TWA tests by both ECG and
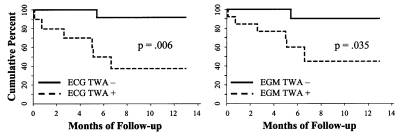
EGM, and 1 pt had negative (-) TWA tests by both ECG and EGM. The figure shows
that both ECG TWA (p = .006) and EGM TWA (p = .035) predicted event-free
survival rate from appropriate ICD therapies. Conclusion: In ICD pts,
ECG and EGM TWA have a high degree of concordance and similar predictive value
for spontaneous VT/VF. This suggests that they represent the same
pathophysiological process. Further studies are needed to determine if EGM TWA
can serve as an immediate warning for VT/VF in ICD pts.