|
Author
Block:
|
Derek
V. Exner, MD, MPH, Karen Cowan, RN, George Wyse, MD, PhD, Brent Mitchell,
MD, Robert S. Sheldon, MD, PhD, Anne M. Gillis, Katherine M. Kavanagh, MD
and Henry J. Duff, MD. University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada
|
|
BACKGROUND.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) improves functional capacity in
many patients with highly symptomatic heart failure, left ventricular
dysfunction & conduction delay. However, there is significant variation
in individual response to CRT. Given the cost & complexity of CRT,
simple means to identify patients most likely to respond to CRT are
required. The presence of microvolt beat-to-beat alterations in cardiac
repolarization (T wave alternans; TWA) is related to cellular calcium flux.
Since altered calcium handling is central in heart failure, we hypothesized
that TWA assessment may aid in identifying patients likely to respond to
CRT.
METHODS. Consecutive patients (n = 23) undergoing CRT had baseline TWA
evaluation performed (RV pacing @ 109 bpm) via a commercial system
(Cambridge Heart). Their mean age was 69 years, mean ejection fraction (EF)
0.21, mean QRS duration 172 msec & 74% had ischemic heart disease. All
had NYHA class III (61%) or IV (39%) symptoms despite optimal medical
therapy. Patients were followed for an average of 18 months post-CRT
implantation.
Patients were categorized as clear responders if they improved ≥2
NYHA classes & had an absolute increase in EF ≥ 0.10. There were
12 (52%) clear responders. Baseline EF, QRS duration, & heart failure
severity was similar in the 2 groups (p > 0.2). Patients who clearly
responded had greater total TWA voltage (35±19 μV) than patients who did not
(11±10 μV; p
=0.001). TWA voltage was useful in identifying CRT responders (odds ratio
1.12, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.23; p=0.02; FIGURE). The positive & negative
predictive values for identifying dramatic CRT responders were 73% &
67%, respectively. 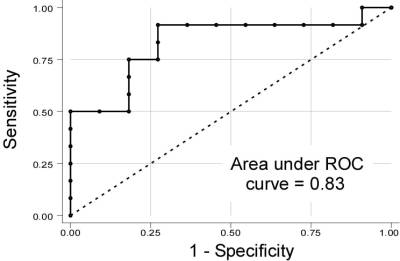
CONCLUSION. TWA assessment may be useful in identifying patients more &
less likely to respond to CRT. Additional studies evaluating the predictive
utility of TWA assessment in identifying CRT responders are required.
|